The causes of thrombosis can vary depending on whether it affects an artery or a vein. Arterial thrombosis can be caused by damage to the artery wall, such as atherosclerosis, or by risk factors such as smoking or hormonal birth control. Vein thrombosis can be caused by cancer, infection, inflammation, varicose veins, prolonged sitting, injury, surgery, or prolonged immobilization.
What are the symptoms of venous or arterial obstruction?
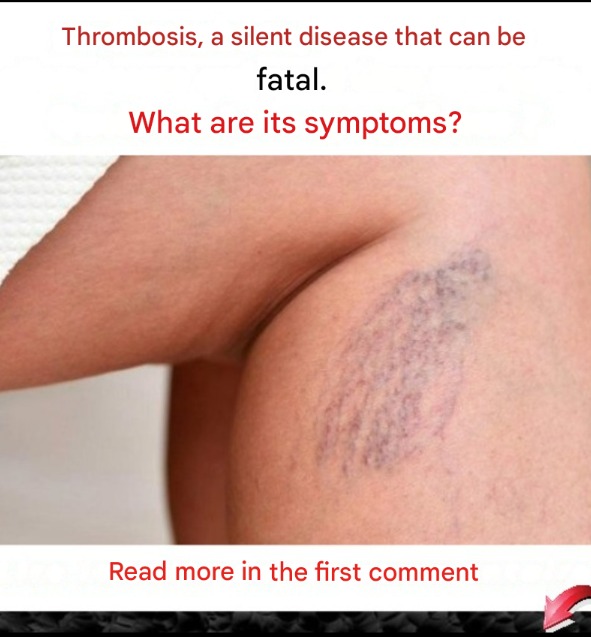
Symptoms of venous thrombosis depend on the location of the thrombosis. If the thrombosis occurs in a lower limb, symptoms may include pain, hardening, redness and warmth of the affected area, bluish or whitish discoloration and edema formation. However, in 50% of cases, deep vein thrombosis may be asymptomatic. If the thrombosis is arterial, it may cause symptoms depending on the area affected. For example, if the thrombosis affects a cerebral artery, the symptoms may resemble those of a stroke. If the thrombosis affects a coronary artery, the symptoms may resemble those of a heart attack. Arterial thrombosis affecting the lower limbs may cause sharp pain, paleness, coldness and absence of pulse in the affected area. If thrombosis forms in the arteries that supply the digestive tract, it can cause persistent abdominal pain.
Who are the people most affected by this disease?
continued on next page: